- Start
- Wissenswertes für Ihr Bauprojekt
Interesting facts for your building project
Immerse yourself in the world of knowledge. Here you will find all the information you need for your construction project. From waterproof concrete and the stress classes to relevant DIN standards and the various water exposure classes. Get valuable information for the success of your construction project.
Waterproof concrete and load classes
Find out here which class of waterproof concrete is suitable for which application. The main difference lies in the intensity and duration of exposure to water.
Load class 1
In this class, waterproof concrete protects structures with a low to moderate water load. This means that the concrete is mixed and processed in such a way that it can withstand normal to slightly increased moisture levels. This usually refers to buildings that could come into contact with water but are not exposed to constant or intensive loads.
Load class 2
For structures with a significantly higher water load, watertight concrete of load class 2 is used. Increased water load means: structures that are exposed to permanent water contact or increased moisture, for example swimming pools, drinking water tanks or construction projects in water-rich environments. Here, watertight concrete must be particularly resistant in order to prevent the penetration of water over long periods of time.
DIN standards
DIN standards are important in order to be prepared for certain effects or conditions on construction sites. For example, a soil survey may specify that construction should be carried out in accordance with DIN 18533. Or: The building has rooms in the basement areas that are particularly worthy of protection, such as archives, server rooms, etc. Here too, waterproofing in accordance with DIN 18533 is mandatory.
DIN 18533
DIN 18533 is a standard that specifies requirements for the waterproofing of components in contact with the ground, such as basement walls, foundations and penetrations in buildings. It defines the various water exposure classes and specifies the necessary protective measures to prevent the ingress of water. As a protective measure, liquid or sheet waterproofing materials are also applied to the exterior walls. This may be important for you as a building owner, builder or contractor for the following reasons:
Product specifications
The standard specifies the requirements for the water impermeability of building components in contact with the ground. Cable and house penetrations fall into this category and must meet the relevant requirements to prevent water ingress and protect the integrity of the building structure.
Quality assurance
The standard also serves as a quality standard for the waterproofing of buildings. As a manufacturer, we produce in accordance with this standard and thus ensure that our products meet the requirements for water impermeability.
Reliability
If you as a building owner really want to reliably and effectively prevent water from entering your building, we recommend our products - i.e. from a manufacturer that complies with the legal standard.
Legal requirements
Many countries and regions require building owners by law to comply with building standards such as DIN 18533. Use products that comply with the relevant standards, avoid legal problems and ensure that you can complete your project on schedule.
.png?width=1200&length=1200&name=DIN-standards-en%20(1).png)
As professionals in the construction industry, it is essential to always be up to date with the relevant standards. One of these is DIN 18533, which deals with the waterproofing of building components in contact with the ground. DIN 18533 specifies detailed requirements and recommendations for the planning, execution and quality assurance of waterproofing measures. This applies to various areas such as basement walls, foundations and floor slabs. By complying with this standard, we not only ensure the longevity of structures, but also effective protection against ground moisture and backwater. This is crucial for the quality of construction and the satisfaction of our customers. As experts, we set the standards high and always strive to implement best practice in construction. Knowledge and application of DIN 18533 is an integral part of our commitment to quality and professionalism.
.png?width=1200&length=1200&name=DIN-standards-en%20(2).png)
DIN18533-1 describes the requirements, planning and implementation principles for the waterproofing of components in contact with the ground. For the planning phase, this means that all relevant criteria must be taken into account. Criteria are for example
- Water exposure classes
- Crack classes
- Room utilization classes etc.
DIN18533-1 describes that these must be determined and weighed up in advance! Only then are the product requirements in DIN18533-2 and 3 applied.
.png?width=1200&length=1200&name=DIN-standards-en%20(3).png)
.png?width=1200&length=1200&name=DIN-standards-en%20(4).png)
Water exposure classes
This overview will help you to better understand the protective effect of our products against different water-related situations.
W2.2-E: pressing water
Stagnant water of more than 3 m (pressing water): Even if the water rises higher due to damming or other reasons, our products provide the necessary protection.
W1-E: non-pressing water
For highly permeable soils and materials: Areas in which there is no permanent accumulation of water. Drainage systems are in place here to regulate the flow of water.
W2.1-E: moderately pressing water
Backwater up to 3 m (moderately pressing water): If water presses against the building component, for example in areas with less water-permeable subsoil, our products offer reliable protection. Groundwater up to 3 m (moderately pressing water): Our products also protect against rising groundwater.

Elastomers
On construction sites, choosing the right materials is crucial to the success of a project. At UGA, we understand the requirements and challenges that our customers face on construction sites, which is why we offer awide range of elastomers inconjunction with our products. On construction sites, choosing the right materials is crucial to the success of a project.At UGA, we understand the requirements and challenges that our customers face on construction sites, which is why we offer a wide range of elastomers. We now explain which elastomers we offer in conjunction with our products and where the individual strengths lie!

Elastomers are polymeric materials that can deform under the influence of external forces, but return to their original shape once the forces have been relieved. These elastomers are known for their elasticity and flexibility, making them ideal for use in our products. In our cases, we use a wide variety of elastomers in our products such as rubber press seals (GPD), ring-space seals (RRD) or system inserts, depending on the customer's wishes and requirements. For example, these elastomers, also known colloquially as rubbers, are pressed between the metal plates in our rubber press seals so that core drill holes or similar can be optimally sealed gas- and watertight.
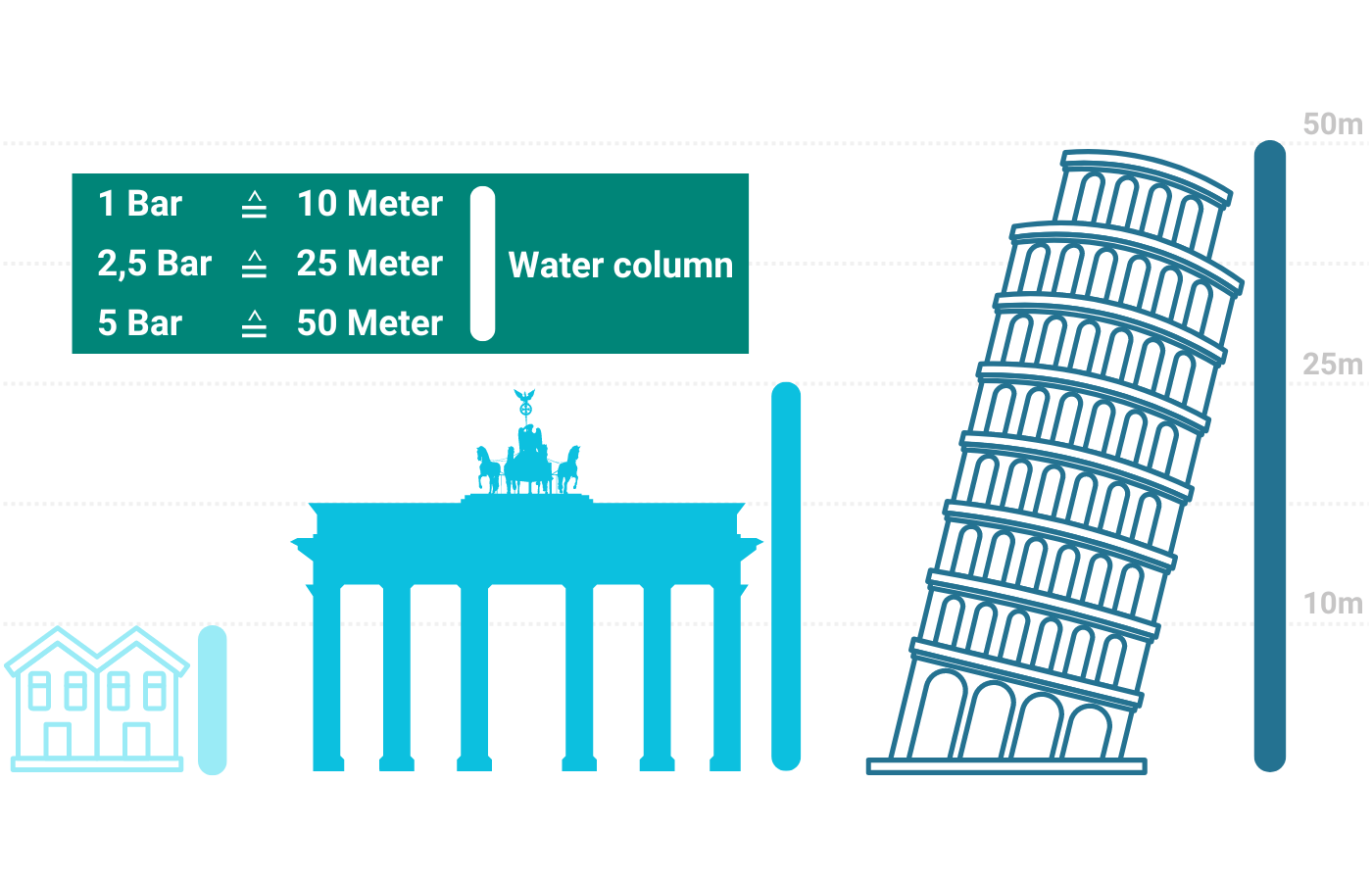
What does 2.5 bar water pressure mean?
How often do we hear the sentence: "I'd better play it safe and take the 5 bar version!" This belief that more is better and safer often leads to customers buying the more expensive versions that they don't actually need.
To better understand the topic, let's first take a look at the basics. Bar is a unit of measurement for pressure. One bar is roughly equivalent to the pressure generated by a 10 meter high column of water. This means that when we talk about 5 bar water pressure, imagine that the water forms a column 50 meters high. That's a considerable amount of pressure, far in excess of what is actually needed in most applications. See for yourself.
Stainless steel
What is the difference between V2A and V4A? We often encounter this question when it comes to choosing between V2A and V4A stainless steel. We bring light into the darkness! The difference lies in the composition: V2A consists of chrome, nickel and steel and offers outstanding corrosion resistance, especially against moisture, which ensures a long service life. V4A, on the other hand, contains molybdenum in addition to the main components. This additional material gives the stainless steel enhanced protection against even more aggressive environments such as salt water, chlorine and chemicals. No matter which variant you choose, we can provide you with high-quality stainless steel that meets your requirements.

UGA Newsletter
Always stay up to date! Here you can find out interesting facts from the world of sealing and fire protection systems - always with a focus on user benefits and with a high level of practical relevance. You will be the first to know about new products and the latest company news.
Reliably protect values
We are at your side!
Our contact
UGA SYSTEM-TECHNIK GMBH & CO. KG
Heidenheimer Str. 80-82
89542 Herbrechtingen
Germany
